A Discipline Divided
As I reflect on the literature we have read this semester, I realize that the
state of our beloved field reflects the current state of our beloved country: we’re divided. The 2016 presidential election was over a week ago, and it seems that individuals across the United States who are voicing their distress over and disgust for our  current president-elect will continue to do so long after inauguration day in January. The debates in the field of English over foundations, theories, practices, and approaches likewise carry on. And, like politics, our English-related debates have developed over decades and continue to persist. Literary studies, for example, oppresses composition with its humanist approach to pedagogy, thereby deeming literary studies as superior and composition as “a barely tolerated stepchild (cited in Gaillet, p. 164). Tensions persist, but in the midst of them, we—citizens and scholars—must still work to be productive.
current president-elect will continue to do so long after inauguration day in January. The debates in the field of English over foundations, theories, practices, and approaches likewise carry on. And, like politics, our English-related debates have developed over decades and continue to persist. Literary studies, for example, oppresses composition with its humanist approach to pedagogy, thereby deeming literary studies as superior and composition as “a barely tolerated stepchild (cited in Gaillet, p. 164). Tensions persist, but in the midst of them, we—citizens and scholars—must still work to be productive.
Our effort to be productive ensures that we continue to move forward as a field, advancing the work of our predecessors in spite of those who challenge us. WAC is a response to the tensions in and surrounding our field (Depew, personal communication, October 26, 2016). It works to cultivate students’ understanding of the discourse of a discipline so they may write across the disciplines successfully.
A Major Question in WAC
Scholars in this field often question whether goal-oriented progress, or the use of outcomes, increases the tension that exists between the disciplines. Interestingly, institutions who utilize a WAC model each designate their own outcomes to work toward, but for Condon and Rutz (2013), successful WAC programs are supported by a complex infrastructure that supports general education and first-year seminar goals (p. 359). Disciplines across the university as well as first-year programs across institutions, therefore, need to be in conversation with each other for WAC programs to thrive. For Fishman and Reiff (2015), first-year composition (FYC) has become less isolated from the rest of the university due to WAC (p. 69), so this expectation should not seem so ambitious.
WAC Objects of Study

The field seems to accept that there’s “no one writing course that can accomplish the curricular or pedagogical goal of teaching students ‘how to write’” (Reiff, et al., 2015, p. 121). For this reason, various curricula have become sites of study to understand how students are learning and what they are doing with that learning beyond FYC (Ballif; Boone, et al.; Kinney & Costello). These sites serve as just one of the several objects of study (OoS) used by the field to measure the effectiveness of various WAC pedagogies. Of course, we still lack interdisciplinary conversation with our colleagues outside the field of composition (and some of these colleagues may still be scholars of English), so other OoSes are often focused within composition classrooms; students, their writing, and instructor pedagogy allow us to gain insight into the effectivity of specific WAC curricula.
For example, the use of writing to learn exercises in the classroom prompts students to think through key ideas and concepts. We use experimental studies, administering pre-tests and post-tests to allow us to capture the development of skills that occurs in students during the course of a semester. We also use case studies of students, which are designed to prompt students to talk about how the writing is shaping their understanding of the content of the discipline. Case studies are not limited to students, of course; at times, case studies of instructor pedagogy have proven to provide valuable insight into the learning and writing environment (Bacon; Beaufort; McCarthy; Nelms & Dively; Sternglass; Yancey, Robertson, & Taczak).
Our goal is to make the learning and teaching experience transparent for both the student and the teacher. Doing so could lead to not only successful transfer from first-year composition to other writing situations for students, but it could also enable instructors to enhance their  instructional strategies to further support transfer (e.g. student understanding of context in classes outside of and beyond FYC). These benefits, however, can only achieve their potential through communication and cooperation across the disciplines. So with such potential benefits that could result from WAC, I can’t help but wonder why the disciplines remain divided. Why do we resist each other? Or better yet, why do other fields (English and non-English) continue to resist composition? It’s ironic to me that the university often prides itself in its interdisciplinarity, but when it comes to reaching across the aisle to a different discipline, power often takes priority over cooperation.
instructional strategies to further support transfer (e.g. student understanding of context in classes outside of and beyond FYC). These benefits, however, can only achieve their potential through communication and cooperation across the disciplines. So with such potential benefits that could result from WAC, I can’t help but wonder why the disciplines remain divided. Why do we resist each other? Or better yet, why do other fields (English and non-English) continue to resist composition? It’s ironic to me that the university often prides itself in its interdisciplinarity, but when it comes to reaching across the aisle to a different discipline, power often takes priority over cooperation.
References
Condon, W. & Rutz, C. (2013). A taxonomy of writing across the curriculum programs: Evolving to serve broader agendas. Conference on College Composition 64(2), 357-382.
Fishman, J. & Reiff, M. J. (2015). Taking the high road: Teaching for transfer in an FYC program. In M. J. Reiff, et al. (Eds.), Ecologies of writing programs: Program profiles in context (pp. 68-90). Anderson, SC: Parlor Press.
Gaillet, L. L. (2009). A socially constructed view of reading and writing: Historical alternatives to “bridging the gap.” In L. Ostergaard, J. Ludwig, & J. Nugent (Eds.), Transforming English studies: New voices in an emerging genre (pp. 163-178). West Lafayette, IN: Parlor Press.

 While over 200,000 American troops were fighting abroad in the Vietnam War by the 1970s, American education at home was taking a shift toward science, technology, engineering, and math studies (STEM) in order to better prepare a workforce for post-industrial society. Writing education, as a result, also shifted, seeking to identify pedagogical approaches for getting students to think about the content in their various courses and the interrelatedness of writing between them. According to Kevin Eric DePew, Associate Professor of English at Old Dominion University, Writing Across the Curriculum (WAC) emerged as a product of the 70s and a response to this writing studies need: “Though they weren’t using the acronym STEM yet, you had the sense of making everything very STEM-like, or practical, including writing” (personal communication, October 26, 2016). In a post-industrial society in which services were dependent upon intelligent designers and users of technology, practicality in writing meant that the consumers, or students, would be able to see the usefulness and transferability of their writing skills across contexts.
While over 200,000 American troops were fighting abroad in the Vietnam War by the 1970s, American education at home was taking a shift toward science, technology, engineering, and math studies (STEM) in order to better prepare a workforce for post-industrial society. Writing education, as a result, also shifted, seeking to identify pedagogical approaches for getting students to think about the content in their various courses and the interrelatedness of writing between them. According to Kevin Eric DePew, Associate Professor of English at Old Dominion University, Writing Across the Curriculum (WAC) emerged as a product of the 70s and a response to this writing studies need: “Though they weren’t using the acronym STEM yet, you had the sense of making everything very STEM-like, or practical, including writing” (personal communication, October 26, 2016). In a post-industrial society in which services were dependent upon intelligent designers and users of technology, practicality in writing meant that the consumers, or students, would be able to see the usefulness and transferability of their writing skills across contexts.
 represented in WAC is rhetorical theory, which Bazerman and Russell (1994) discuss in their introduction to Landmark Essays. WAC was evident in the rhetorical traditions of the Ancient Greeks as it is today, and for Bazermen and Russell, there is a long tradition in rhetorical theory to support the reasons we have WAC.
represented in WAC is rhetorical theory, which Bazerman and Russell (1994) discuss in their introduction to Landmark Essays. WAC was evident in the rhetorical traditions of the Ancient Greeks as it is today, and for Bazermen and Russell, there is a long tradition in rhetorical theory to support the reasons we have WAC. In
In 
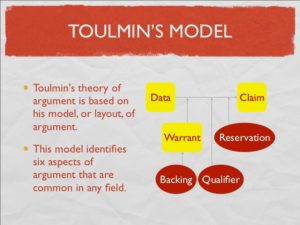
 The authors note that the evidence from their study suggests that the majority of the twelve students improved their ability to articulate claims and support them with evidence in FYC. In the WAC courses, the authors found that “[w]hile the students in this study encountered in WAC a diverse variety of genres, most of those genres required them to support claims with evidence. In this regard, students appeared to benefit from related instruction in FYC. That is to say, students’ development of ability to articulate and support claims in FYC appeared directly related to their ability to do so in their later WAC courses” (p. 46). But after reading this article, I have several questions for the authors about their
The authors note that the evidence from their study suggests that the majority of the twelve students improved their ability to articulate claims and support them with evidence in FYC. In the WAC courses, the authors found that “[w]hile the students in this study encountered in WAC a diverse variety of genres, most of those genres required them to support claims with evidence. In this regard, students appeared to benefit from related instruction in FYC. That is to say, students’ development of ability to articulate and support claims in FYC appeared directly related to their ability to do so in their later WAC courses” (p. 46). But after reading this article, I have several questions for the authors about their